What is IP rotation, and how does it work?


Have you ever been blocked from accessing a website, noticed different prices for the same product, or felt concerned about websites tracking your online activity? These issues often stem from how websites recognize and respond to your IP address—the unique string of digits associated with your connection.
You need an IP address to connect to the internet, so you can’t browse without it. But you can change it to gain more control over your browsing experience. That’s where IP rotation comes in handy. IP rotation is a technique that changes your device’s IP address at regular intervals, making it appear as though your connection is coming from different sources. With the right tool, you can also make it appear as if you’re connecting from another location.
We’ll guide you through how IP rotation works so you can determine whether it is right for you. Once that’s cleared up, we’ll show you three different ways to rotate your IP address—so you can choose whether using a VPN, proxy server, or your ISP is the right method for you.
What is IP rotation?
IP rotation is the process of changing your IP address at set intervals or with each new connection. Instead of maintaining a single, static IP address, your device regularly switches to a new one. This makes it harder for websites and services to track your activity, as they can’t link all that activity to one IP address to build an accurate profile of you.
Many online services recognize and log people’s activity based on their IP addresses. When your IP address remains the same, websites can potentially limit your access or display different content based on the past activity and data they associate with your IP address. IP rotation helps prevent this by making your online presence less predictable.
Depending on the method, you can even rotate between IP addresses from different locations, letting you mask your real location. This can also help you access localized content and services. As every IP address is registered to a specific region, platforms can easily block users or change content based on peoples’ IP addresses. Therefore using an IP address registered to a different state or country will let you browse as if you’re a local.
How IP rotation works
IP rotation relies on a system that assigns your device a new IP address at scheduled intervals or under certain conditions. There are three primary ways this happens:
- VPN-based rotation: When you connect to a VPN, your IP address changes to the VPN server’s IP address. If you reconnect or switch between different VPN servers, your IP address will change again. Some VPNs automatically rotate IP addresses within the same server location, while others allow manual selection.
- Proxy-based rotation: Proxies route your connection through servers with different IP addresses. They often use a pool of available IP addresses that rotate either every time you connect to a proxy server or with every request sent through your connection.
- ISP-based rotation: ISPs typically assign dynamic IPs to their customers. These IP addresses may change periodically, usually when the customer’s router is switched off and on again.
Setting up a rotating IP address doesn’t need to be complicated. In fact, it’s as easy as subscribing to ExpressVPN, installing the app on your device, and turning on the VPN. You can regularly switch to a new IP address by either connecting to a new VPN server on the app or relying on ExpressVPN’s ShuffleIP feature that automatically changes your IP address with every new request.
Static vs. dynamic vs. rotating IPs
We’ve mentioned a few different kinds of IP addresses so far, but that might have left you wondering how they all fit together. Here’s a quick reference table to help clear things up:
| Type of IP address | Static IP | Dynamic IP | Rotating IP |
| Definition | A fixed IP address that does not change and is assigned to only one customer—either by an ISP or third-party service. | A non-fixed IP address that ISPs assign to their customers. An ISP can assign a different IP address to a customer periodically, though not necessarily as frequently as with an IP rotation system. Customers can typically also change the dynamic IP address assigned to them by reconnecting their router. | A system owned by a third party that owns multiple IP addresses, such as a VPN or proxy service. When a device connects to the system, it replaces the device’s IP address, and then frequently swaps the IP address with a different one. These IP addresses can be defined as dynamic IP addresses since they’re not fixed. |
| Setup | Fixed IPs are associated with one location and customer for the duration of the agreement between that customer and the service providing the IP address. ISPs and third-party services like VPNs can provide static IP addresses. As an example, ExpressVPN lets you add a dedicated IP when you subscribe. | Each IP address is associated with the customer’s location and identity (via their ISP contract), even if they switch to a new dynamic IP address. | Depending on how the system is set up, IP addresses may be shared between multiple people simultaneously. If the service prioritizes anonymity, none of the IP addresses a person uses will be associated with their identity or real location. |
| Use case | Businesses, hosting services, and remote workers who need to maintain consistent access to information or stakeholders will typically use a static IP address. To do that, they have to request one from their ISP or use a third-party service, often at an extra charge. | Most ISPs automatically assign dynamic IP addresses to their customers as this makes it easier for ISPs to manage their services. | Anyone looking to change their IP address frequently. This could be for reasons related to privacy or access. Those wanting to use a system that rotates their IP addresses typically need to subscribe to a third-party service like a VPN or proxy. |
Read more: Learn the deeper differences between static and dynamic IP addresses, and how they work.
VPN rotation vs. proxy rotation—What’s the difference?
Both VPNs and proxies can rotate IP addresses, but they function differently:
- VPNs encrypt your internet traffic while rerouting your traffic through one of its servers, replacing your IP address with the server’s IP address. This makes VPNs ideal for people who prioritize privacy and security—including additional privacy against ISP monitoring.
- Proxies only reroute your traffic through one of its servers, replacing your IP addresses with one it owns. Proxies do not provide encryption or other anonymizing measures, making them more suited for tasks like web scraping where security and privacy are less of a concern.
How often do VPNs rotate IP addresses?
IP rotation frequency varies depending on the VPN provider. Some VPNs automatically swap your IP address after a set period, while others only change your IP address when you manually switch servers. Most VPNs also use “shared IPs,” meaning they cycle the pool of IP addresses assigned to each VPN server between everyone connected to that server for added anonymity. As a result, you’ll likely still get a different IP address even when you reconnect to the same server.
What are the risks of having a rotating IP address?
While rotating IPs can improve your privacy and help you bypass restrictions, there are some potential downsides:
- Frequent verification requests: Some websites may flag frequent IP address changes as suspicious, prompting more CAPTCHA challenges or login verifications.
- Inconsistent browsing experience: Some services personalize content based on location, and a rotating IP may disrupt recommendations, language settings, or regional access.
- Temporary blocks: If a platform has flagged an IP address from a shared rotation pool for abuse, you may inherit its reputation and encounter access issues. You can easily solve this problem by switching to another IP address.
Why is IP rotation important?
IP rotation serves several practical purposes, from enhancing privacy to bypassing regional restrictions. Here are some of the most common reasons people use it:
Prevent online tracking and fingerprinting
Your IP address is a key identifier that websites, advertisers, and even your ISP can use to track your online activity. By frequently changing your IP, you make it harder for anyone to link your browsing habits to a single identity. VPN-based IP rotation is particularly effective for maintaining privacy, as it also encrypts your traffic to prevent ISP monitoring and other kinds of digital snooping.
Avoid content blocks and dynamic pricing
Streaming services, online stores, and news websites often restrict access or change their content based on people’s location. Since an IP address reveals your general geographic area, rotating between IP addresses from different regions can help you access content that may otherwise be unavailable in your country.
Many websites also adjust their pricing based on your browsing history, location, and demand in your area. For example, airlines may show different prices to people in different cities or states for the same flight. By rotating your IP address, you can check for price differences and potentially get better deals.
Avoid IP bans and rate limiting on websites
Some websites impose access limits per IP address, such as restricting the number of times you can view an article before hitting a paywall. Websites can also ban your IP address if it has a poor reputation based on someone’s past actions, which locks you out entirely. By rotating your IP address, you can reset these limits and continue browsing without interruptions.
Enhanced security against cyber threats
Cybercriminals often attempt to track users through their IP addresses to gather information and launch targeted attacks. Using the same IP over long periods can expose you to DDoS attacks, IP-based hacking attempts, and malicious tracking intended to learn your identity or movements.
Rotating your IP address reduces the chances of being targeted by such attacks. Using a VPN for IP rotation adds an extra layer of protection, as it not only changes your IP address but also encrypts your traffic, making it harder for attackers to intercept or monitor your online activity.
Read more: How to change IP locations by setting up a VPN on your router
Can IP rotation be used for social media automation?
Some people may promote IP rotation as being helpful when managing multiple social media accounts or automating tasks like posting, following, or engagement. However, social media platforms have strict policies against automated behavior, and using IP rotation in this way carries risks.
Here’s what you need to know:
- IP rotation alone won’t prevent detection. Social platforms use multiple tracking methods beyond detecting IP addresses, such as device IDs, cookies, and behavioral analysis.
- Frequent IP address changes may trigger security alerts. If an account logs in from multiple locations in a short time, it may be flagged for suspicious activity.
- Proxies are often used for automation, but they don’t offer privacy. Many automation tools rely on proxy-based IP rotation, but this doesn’t provide encryption or protect your personal data.
How to rotate your IP address with a VPN (step-by-step guide)
A VPN provides the easiest and most secure way to rotate your IP address. When you connect to a VPN, the VPN server replaces your IP address with its own. Most VPN services provide access to a pool of IP addresses across multiple server locations, letting you switch between them as needed. Follow the steps below to set up IP rotation in a couple of minutes.
- Subscribe to ExpressVPN and install the correct app for your device.
- Log in to your account on the VPN app.
- Connect to a VPN server. You can let the VPN choose the nearest server to your location or choose any server located in one of the 100+ countries in our network.
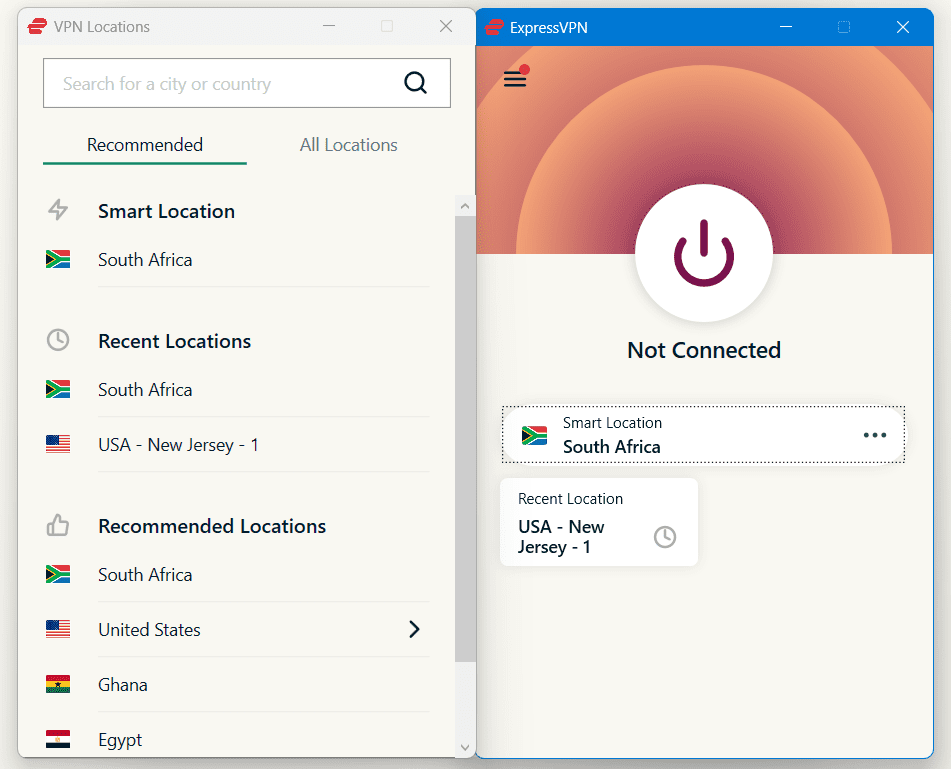
- The app will display you’re connected to the VPN server and list the server assigned to your device.
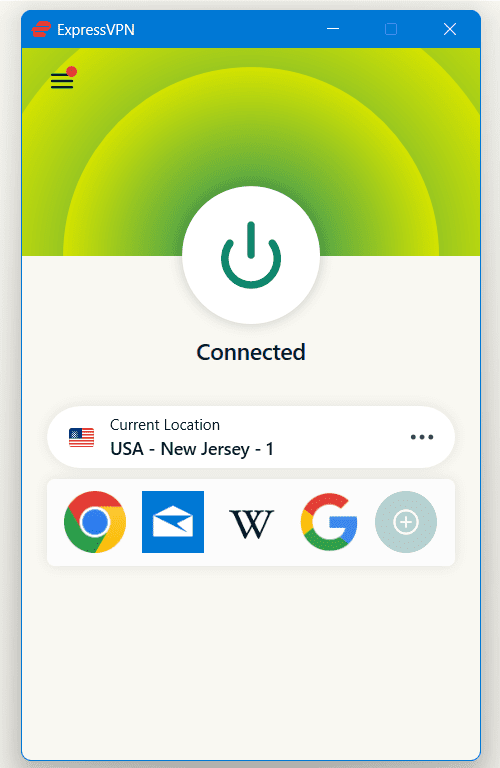
- ExpressVPN’s ShuffleIP feature automatically gives you a different IP address for every web server or website you access. This feature automatically kicks in on server locations where ShuffleIP is available.
- If you’re connected to a server that doesn’t support ShuffleIP, you can manually switch to a different server in the app to get a new IP address.
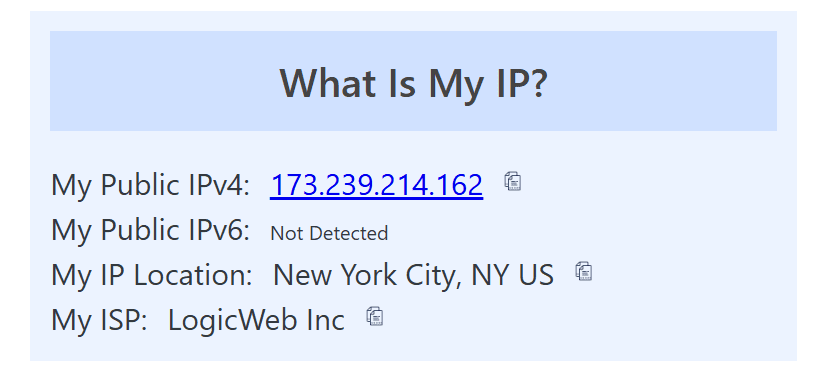
- You can use an IP-checking website (such as WhatIsMyIP) to confirm your IP address has changed.
Manual vs. automatic IP rotation—Which one is better?
VPNs typically offer two methods for rotating IP addresses. The best choice depends on your needs.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
| Manual IP Rotation | Lets you select specific server locations, giving you full control over when and where your IP changes. | Requires manual intervention and it can disrupt your connection if you’re switching frequently between different servers. |
| Automatic IP Rotation | These IP address changes happen without effort on your part. This method can further improve your anonymity by rotating your IP address regularly within the same server location. | Not all VPNs offer this feature and some websites may temporarily block repeated IP changes. |
How to check if your VPN is rotating your IP?
If your VPN offers IP rotation, you can confirm it’s working by checking whether your IP address changes while connected. Follow these steps to test it:
- Connect to your VPN and check your current IP address. You can find it in your VPN app or by visiting an IP-checking site like WhatIsMyIP.
- Reconnect to the VPN server by either disconnecting and reconnecting or switching to a different server.
- Check your IP address again to see if it has changed. If it’s different, your VPN is successfully rotating your IP.
How does time-based IP rotation work?
Time-based IP rotation automatically assigns a new IP address at regular intervals. Depending on the provider, this could happen every few minutes, every time you start a new session, or after a specific amount of data usage. This method helps prevent websites and services from tracking your activity based on a single IP address.
Some services rotate IP addresses within the same geographic location, meaning your virtual location stays the same while your IP changes. Others may rotate IPs across different locations, allowing you to appear as if you’re connecting from different regions. The frequency and method of rotation depend on the tool being used—whether it’s a VPN, proxy, or ISP-based system.
While time-based IP rotation can improve privacy, frequent changes may trigger security checks on some websites, such as CAPTCHAs or login verifications.
Alternatives to VPN IP rotation—Proxy & ISP rotation
While VPNs offer one of the most effective ways to rotate your IP address while maintaining security and privacy, they’re not the only option. Proxies and ISP-based IP rotation offer alternative ways to change your IP address, each with its own advantages and limitations.
What is Proxy IP rotation?
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, replacing your real IP address with one from the proxy’s pool of available IP addresses. Proxy IP rotation means the proxy service automatically assigns you a different IP address at set intervals per session or with each request you make to a website.
How proxy rotation works:
- You connect to a proxy service, which assigns you an IP address from its pool.
- Depending on how the proxy’s IP rotation is set up, your IP address may change per request (every time you load a webpage or make a new connection) or at set intervals (after a certain amount of time).
- The website you visit only sees the proxy’s IP address, not your real one.
People commonly use proxies for tasks requiring high-volume IP rotations, such as web scraping, SEO research, or automated testing.
Sticky vs. rotating proxies: Which one should you use?
Proxies generally fall into two categories:
| Type | How It Works | Best Use Cases |
| Sticky Proxy | Assigns an IP address to your connection that remains the same for the duration of your session. | Managing multiple accounts, social media automation, or tasks requiring a consistent IP address. |
| Rotating Proxy | Assigns a new IP address to your connection with every request or after a set time. | Web scraping, ad verification, and bypassing rate limits. |
Choosing proxy to use depends on your needs. If you require a consistent IP address for a longer session, a sticky proxy is the better option. These proxies assign you an IP address that remains the same for the duration of your session, making them useful for managing multiple accounts, social media automation, or other tasks that require stability.
On the other hand, rotating proxies are ideal for tasks that need frequent IP changes, such as web scraping, ad verification, or bypassing rate limits. With a rotating proxy, your IP address changes either with every request or after a set period, making it harder for websites to track your activity.
If you need anonymity and frequent IP changes, go with a rotating proxy. If you need stability and a single IP for a session, choose a sticky proxy.
What are rotating proxies used for?
Rotating proxies serve several purposes, making them useful for individuals and businesses that need frequent IP address changes. Here are some of the most common use cases:
Web scraping
Many businesses and researchers use rotating proxies to collect data from websites without getting blocked. Since websites often limit the number of requests from a single IP, rotating proxies help bypass these restrictions by assigning a new IP address with each request.
Hiding your IP address
By constantly changing your IP, rotating proxies make it harder for websites, advertisers, and other third parties to track your online activity. This provides an added layer of privacy.
Bypassing restrictions
Some websites block access based on IP addresses, whether for geo-restrictions, rate limits, or security reasons. Rotating proxies help users get around these restrictions by ensuring that each connection request appears to come from a different IP address.
Rotating proxies are especially useful for automation, market research, and security testing, but they don’t provide encryption like a VPN.
Can you combine a VPN and proxy for better IP rotation?
Yes, but with some caveats. Using a VPN and proxy together can enhance your privacy, but doing so has drawbacks and most people don’t need the additional anonymity it provides.
Advantages:
- Adds an extra layer of anonymity by masking both your real and VPN IP address.
- Gives you the ability to access proxy-specific IP pools while maintaining an encrypted connection.
Disadvantages:
- Slows your connection speeds due to your traffic being rerouted twice.
- Increases the risk of connection issues or misconfigurations if you don’t know what you’re doing, as VPNs and proxies aren’t created to work together.
- Adds extra effort on your part as not all VPNs support proxy integration, making it harder or impossible to configure your connection the way you want.
For most people, using a VPN alone is the better option for secure, encrypted IP rotation. However, those who require proxy-specific features (such as web scraping or localized IPs) may benefit from combining both.
ISP-based IP rotation—How to change your IP without VPN or proxy?
Most ISPs assign dynamic IP addresses to customers, meaning their IP addresses change periodically. This is a basic form of IP rotation that doesn’t require additional tools like VPNs or proxies.
How ISP-Based IP Rotation Works:
- Your ISP automatically assigns a dynamic IP address to your network from its pool of available IP addresses. This happens when you first set up your router connection.
- Your IP address may change periodically—some ISPs refresh IP address assignments at regular intervals or when network conditions change.
- Restarting your router can also trigger an IP address change as your ISP may assign a new IP address to your network.
ISP-based rotation is unreliable for people who need frequent IP address changes or need to change their IP location because:
- You can’t control when your IP changes. Some ISPs keep your dynamic IP address assigned to you for long periods unless you disconnect for an extended time.
- Third parties can easily detect your location and behavior online, and customize or restrict your access, using your IP address. Meaning you don’t have much privacy or control.
- You can’t change locations—your new IP address will still be tied to your geographical region.
If you require frequent IP address changes, a VPN or proxy service offers more reliable and flexible options than relying on your ISP.
Common misconceptions about IP rotation
IP rotation is a useful tool for privacy and accessibility, but people have misunderstandings about what it can and cannot do. Below, we address some of the most common misconceptions.
Misconception: IP rotation and VPNs are the same thing
While VPNs and IP rotation often go hand in hand, they are not the same thing. We’ve covered how VPNs can rotate your IP address above, but it’s worth reemphasizing that IP rotation is a feature, not a standalone technology.
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and reroutes it through a secure server, replacing your real IP address with one assigned by the VPN provider. Some VPNs also offer automatic IP rotation, where your IP address changes at set intervals or with each new request.
However, IP rotation can also happen outside of VPNs. Proxies, ISP-based dynamic IPs, and other tools can rotate your IP address without encryption. This is why VPNs provide a stronger layer of privacy and security—they don’t just rotate your IP but also prevent ISPs and third parties from seeing your activity.
If your goal is purely to change IPs, rotating proxies or ISP-based IP changes might work. But if you want privacy, security, and anonymity, a VPN with built-in IP rotation is the better choice.
Misconception: Having a rotating IP means you’re completely anonymous online
While rotating IPs can improve your privacy by making it harder for websites and services to track you, they do not make you fully anonymous. Websites and platforms use multiple tracking methods beyond just your IP address, including cookies and tracking scripts, browser fingerprinting, and account-based tracking.
How to enhance your anonymity with a rotating IP:
- Use a VPN with IP rotation to encrypt your traffic and get anonymous, shared IP addresses.
- Regularly clear your cookies or use incognito mode.
- Disable browser fingerprinting scripts using privacy-focused extensions.
Rotating your IP address adds a layer of privacy, but it’s not a complete solution for anonymity.
Misconception: Rotating your IP address slows down your connection
IP rotation by itself does not inherently slow down your connection, but the method you use to rotate your IP address can impact your speed.
| Method | Effect on Speed |
| VPN-based rotation | Can slow down speeds slightly due to encryption and rerouting, but premium VPNs use fast, efficient, and well-maintained systems to minimize this impact. |
| Proxy-based rotation | Proxies without encryption tend to be faster than VPNs, but proxy connections can be unstable depending on the server quality and distance from the user. |
| ISP-based rotation | No speed impact, unless the ISP applies throttling or experiences server issues. |
How to minimize speed loss with IP rotation:
- Choose a high-quality VPN with fast servers.
- Connect to servers closer to your location for lower latency.
- Avoid overcrowded proxy or VPN servers that can slow down traffic.
While IP rotation may introduce minor connection slowdowns, choosing the right method and reliable service ensures a balance between privacy and performance.
Misconception: Rotating proxies are not suspicious to websites
Websites often detect and block suspicious proxy-related activity, such as rapid IP address changes or requests from known data center IP addresses. However, rotating proxies may use specific techniques to avoid detection, including:
- Residential IP pools. Many rotating proxy providers use IP addresses assigned to real internet users rather than data centers, making it harder for websites to detect that proxy services are using the IP addresses.
- Session-based rotation. Instead of changing IP addresses with every request, some proxies use “sticky sessions” that maintain the same IP address for a set duration before switching. This mimics natural browsing behavior.
- Geo-matching IP addresses. Some proxies assign IP addresses from a pool that matches the user's apparent location, preventing suspicious country-hopping behavior.
- User-agent & header control. Advanced proxies can modify the information in your connection request (such as browser headers and user-agent strings) to blend in with normal traffic.
Websites still have ways to detect automated behavior, but smart proxy configurations are less likely to raise red flags.
How to use IP rotation safely and effectively
Best practices for using rotating IPs safely
How often should you rotate your IP for maximum privacy?
The ideal frequency for IP rotation depends on what you’re using it for. Changing your IP address too often can make your activity look suspicious, while not rotating it frequently enough may reduce the privacy benefits associated with rotating IPs.
| Use Case | Recommended Rotation Frequency | Why? |
| General browsing with added privacy | Every 30-60 minutes. | Prevents long-term tracking without disrupting your session. |
| Accessing content with an IP address based in a different location | Only when needed. | Avoids unnecessary potential IP blocks while maintaining stable access to your preferred platforms. |
| Avoiding website tracking | Every session or new connection. | Makes it harder to link your browsing habits to a single identity. |
| Web scraping or automation | Every request or every few requests. | Prevents rate limits and IP bans but should be done cautiously. |
Avoiding detection—How to use IP rotation without getting blocked
Frequent IP address changes can sometimes trigger security measures, such as CAPTCHAs, login verification prompts, or even temporary bans. Here’s how to rotate your IP address safely while staying under the radar:
- Rotate at natural intervals. Avoid changing your IP address too frequently in a short time, as this can trigger security alerts.
- Mimic human behavior. Automated tools that rapidly refresh pages or submit repetitive actions can be flagged as bots, even with rotating IP addresses.
- Use session-based IP rotation. Instead of switching your IP address with every request, opt for proxies or VPNs that rotate your IP address per session to maintain consistency.
- Clear your cookies and cache. Websites use more than just IP addresses to track you. Resetting your browser session can prevent them from linking your new IP addresses to old activity.
- Pair with a VPN for encryption. If you’re using a proxy, combine it with a VPN to ensure your traffic remains encrypted and secure.
- Use residential IP addresses whenever possible. Websites are more likely to flag data center IP addresses as suspicious, while residential IP addresses appear as legitimate users.
Choosing the right VPN for IP rotation
Not all VPNs handle IP rotation the same way. If you want a seamless experience, look for a premium VPN that offers automatic IP rotation, meaning your IP address changes at set intervals or with every new request. This reduces the chances of websites tracking your activity while keeping your connection stable.
What to look for in a VPN with IP rotation?
Automatic IP rotation
Ensures your IP changes regularly without manual switching.
Large server network
More servers mean more available IPs, reducing the chances of detection.
Obfuscated server capabilities
Helps mask VPN traffic as regular internet traffic.
No-logs policy
Ensures your browsing activity isn’t stored or monitored.
Can you get a dedicated rotating IP?
Some VPN providers offer dedicated IPs, but these are typically fixed to one address, meaning they don’t rotate. However, a few services provide rotating dedicated IPs, which change periodically while remaining assigned to your account. This can be useful if you need a stable yet frequently changing IP for certain online activities.
How to rotate VPN servers for maximum privacy?
If your VPN doesn’t offer automatic rotation, you can manually switch servers to change your IP address. Connecting to different server locations will give you a new IP, but if you prefer to stay in the same region, check if your provider offers multiple servers in one location. Some VPNs also cycle IP addresses within the same server, meaning you don’t always have to switch manually.
Not all VPNs offer automatic IP rotation, but ExpressVPN’s ShuffleIP feature keeps your browsing private by changing your IP with every new request. With a large server network, obfuscated server capabilities, and a strict no-logs policy, ExpressVPN ensures your connection stays secure while rotating your IP seamlessly.
Choosing the right IP rotation method for your needs
Different methods of IP rotation serve different needs, but not all of them offer real privacy. A VPN with automatic IP rotation is the only method that changes your IP while keeping your data secure. Proxies work for automation and scraping but won’t protect your traffic. ISP-based rotation leaves you with no control over when or where your IP changes.
The best option depends on your goals—whether you need privacy, access, or both. Knowing how IP rotation works means you can choose the right method—and avoid the ones that don’t actually protect you.
FAQ: About IP rotation
Is IP rotation legal?
How to test if my IP rotation is working?
Can you choose a specific country when using a rotating IP?
What happens if a website blocks your rotating IP?
How does IP rotation differ from using a proxy?
Can websites detect and block rotating IPs?
What is the best method for rotating IPs?
Why do some websites still recognize me even with a rotating IP?
What should I do if my VPN is not rotating IPs?
Does IP rotation work on mobile networks?
Can you be tracked with a rotating IP?
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN